How BBM Works
Structural diagram
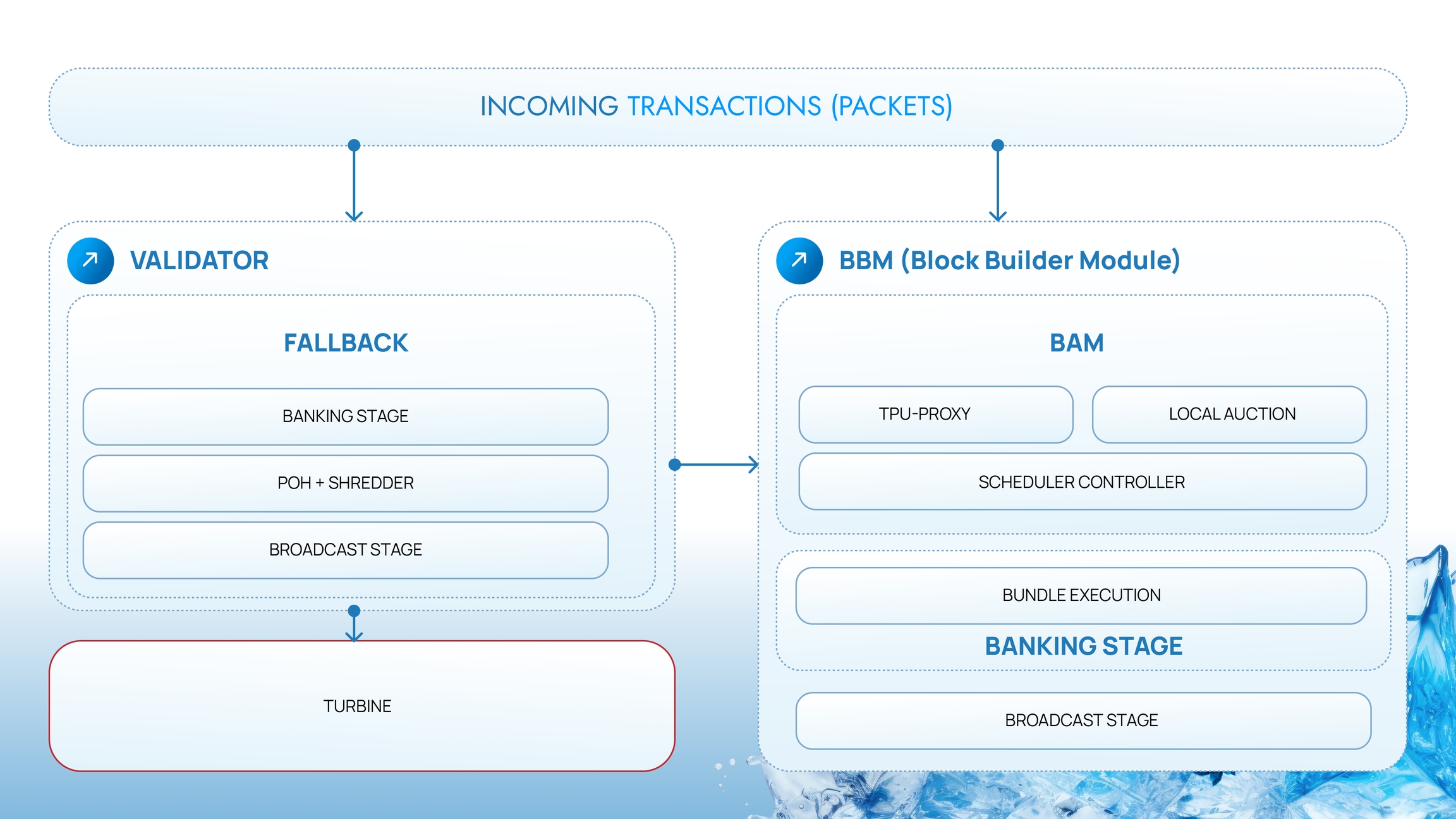
(see image “SHIROI BBM”)
BBM (Block Builder Module) Components:
TPU Proxy
Local Auction
Scheduler Controller
Bundle Execution
Banking Stage
Broadcast Stage
Description of BBM operation:
Incoming transactions enter the system as packets.
BBM accepts the packets and routes them via the TPU Proxy to the local auction, where the execution order of transactions is determined.
The Scheduler Controller then optimizes the execution order.
After the auction, a bundle (a set of transactions) is formed, executed, and passed to the Banking Stage.
The validator receives the completed block, verifies it, and disseminates it via Turbine.
Key feature: Parallel creation of two versions of the block—one by BBM and one by the validator. This increases fault tolerance and overall network reliability.
Last updated